
Installation precautions for air-blown fiber cables
Before commencing cable laying operations,
(1) The microduct system should be inspected to ensure that the minimum bend radius of the cable is not compromised during handling, feeding, laying, and final positioning.
(2) The equipment and all pressure fittings should be inspected.
(3) The laying machine should be inspected to ensure that the tension and compression limits are correctly and accurately set to match the cable being laid.
(4) The radio equipment should be inspected to ensure that all manned locations along the right-of-way are communicating properly and are ready to begin laying.
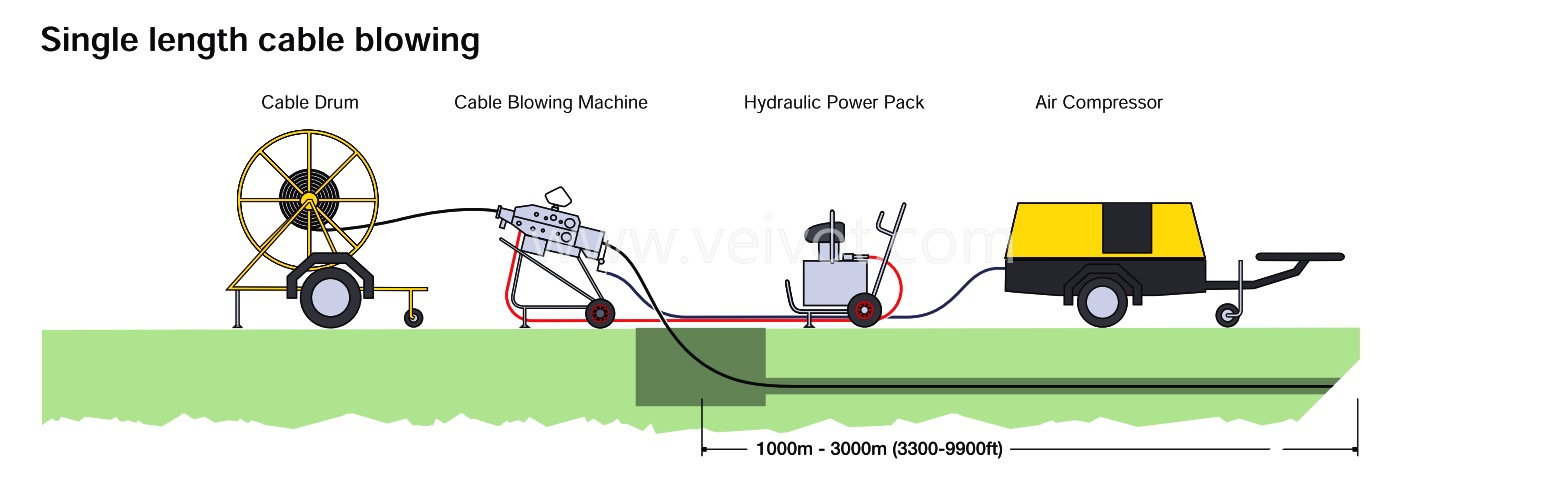
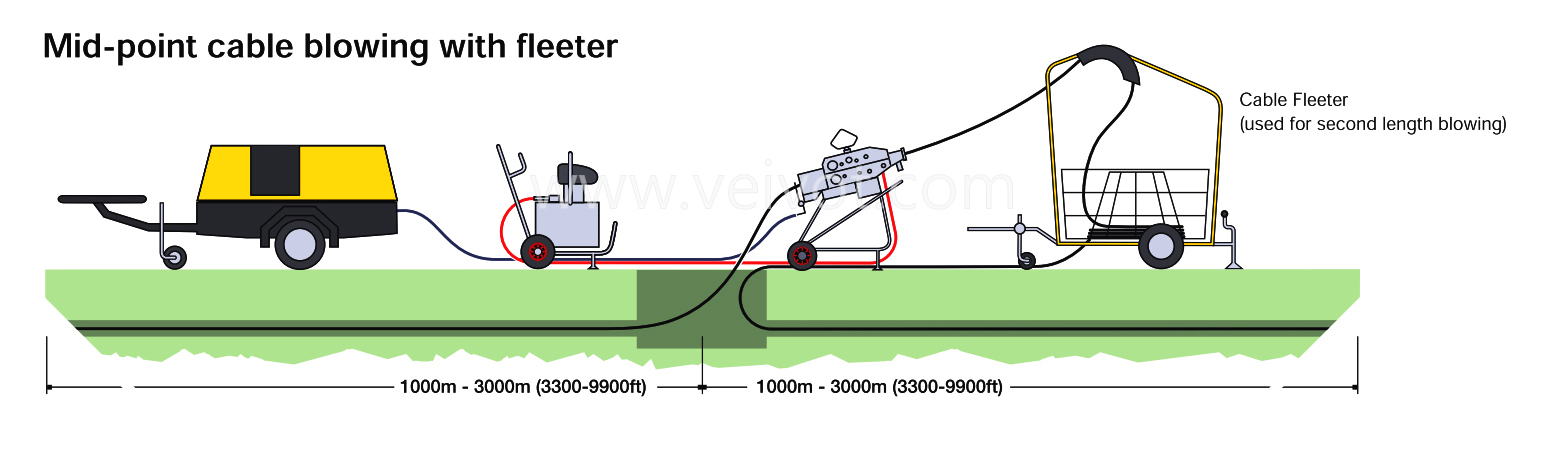
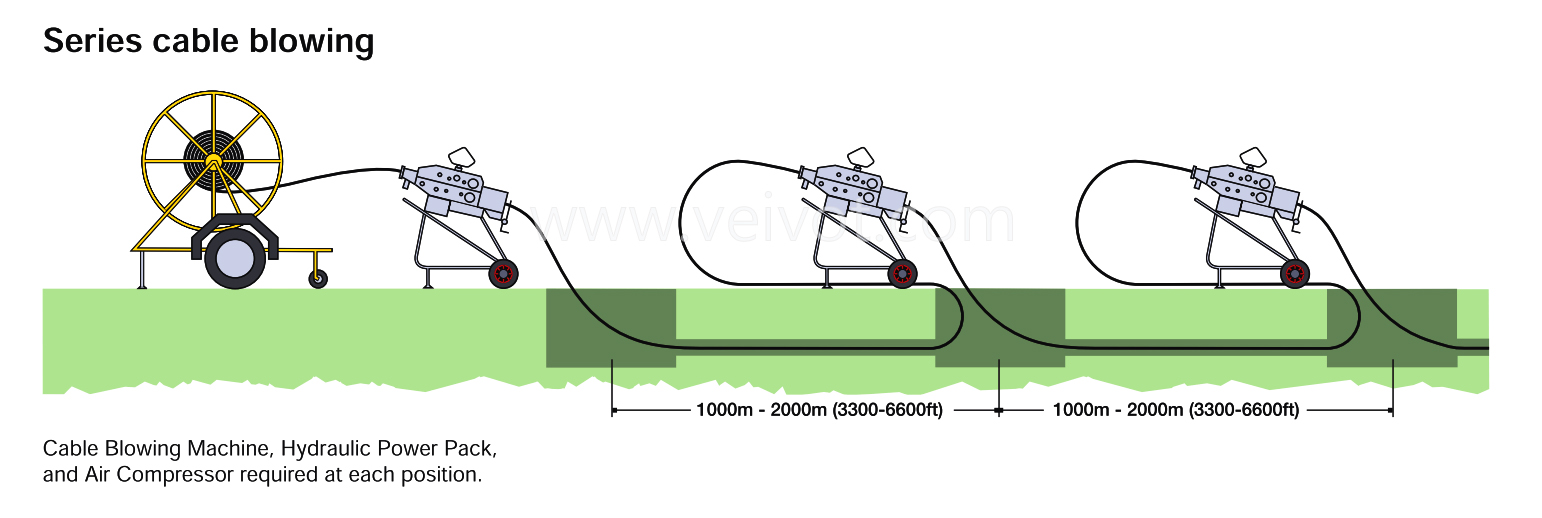
All transitions in and out of manholes should be direct and smooth, without violating any mechanical or geometric limits of the cable.
Air and hydraulic pressures should be set in accordance with the pouring machine manufacturer's instructions. During pouring, the pouring machine should be operated in accordance with its manufacturer's instructions.
The pouring operation should start slowly and remain at a low speed until the pouring process is visibly level. The pouring speed can be gradually increased until a fast but fully controlled speed is reached. Depending on the construction personnel's experience and the geometry of the pouring route, pouring speeds of 30 to 60 m/min (100-190 ft/min) or more can be achieved. VEIVOT and the pouring machine manufacturer recommend that pouring operations be carried out at a safe and controlled speed.
You may encounter some problems when installing air-blown optical cables. Here are some suggestions.
1. The outer protective tube is blocked
Clean the outer protective tube: use a sponge ball to blow into the HDPE pipe to remove the water and dust accumulated along the air-blown optical fiber pipe; survey the location of obstacles in the outer protective tube and remove them.
2. The HDPE optical fiber pipe cannot be air-blown
Check whether the air-blowing equipment is operating normally.
Check whether the air-blowing accessories of the micro-tube air-blowing machine meet the requirements of the outer protective tube, micro-tube outer diameter and the number of air-blown micro-tubes.
3. The air-blowing distance of the micro-tube is not enough
Check whether the outer protective tube is pre-lubricated.
Check whether the outer protective tube is damaged.
Check whether the outer protective tube is clean.
Check whether the seal of the direct-buried micro-tube is intact.
Check whether the size of the micro-tube matches the outer protective tube.
Check whether the blowing position is appropriate.
Check whether the blowing method is correct.
4. The blowing speed of the air-blown optical fiber micro-tube is slow
Check whether the outer protective tube is pre-lubricated.
Check whether the microduct seal is intact.
Check whether the microduct size matches the outer protective tube.
5. Microduct damage during laying
Check whether the microduct laying path is normal.
Check whether the working pressure of air blowing equipment such as optical fiber blowing machine is normal.
Check whether the microduct is always filled with internal air pressure during the air blowing process.
Check whether the equipment thrust exceeds the designed microduct tensile load.
6. Underground microcable cannot be blown
Check whether the air blowing equipment is working properly.
Check whether the air blowing accessories of the microduct air blowing machine meet the requirements of optical fiber air blowing microduct.
7. The air blowing distance of the microcable is not enough
Check whether the communication pipeline has been penetrated and processed.
Check whether the microduct seal is intact.
Check whether the size of the micro air blowing optical fiber matches the microduct.
Check whether the size of the air-blown microcable matches the microduct.
Check whether the optical cable injection mode is correct.
VEIVOT has been committed to the design, manufacture and supply of passive and active components for FTTx fiber optic networks. Everything about VEIVOT is designed to provide efficient, simple and innovative solutions to solve complex tasks. We will continue to innovate and make more contributions to the construction of global fiber optic networks.





 INQUIRY
INQUIRY